Source: JDD Online
The Journal of Drugs in Dermatology recently featured the article, The Relevance of Vitamin D Supplementation for People of Color in the Era of COVID-19, authored by Skin of Color Virtual Update faculty, Pearl E. Grimes MD, and Andrew F. Alexis MD MPH along with Nada Elbuluk MD MSU.
Introduction
African Americans (AA) and other people of color are dying at highly disproportionate rates from COVID-19. The statistics are staggering: in New York City alone, per 100,000 population, death rates in AA were 92.3, and in Hispanics 74.3, compared to 45.2 in Whites and 34.5 in Asians.1 Similar numbers have been reported in other cities and are presumed underestimations, given limited racial/ethnic reporting. In the states currently releasing the number of COVID-19 deaths by race and ethnicity, Blacks make up roughly 13 percent of the population, but 27 percent of the deaths. According to the American Public Media Research Lab, the rate of COVID-19 deaths nationally for Blacks has been reported as twice the rate of deaths of Asians and Latinos in the US and more than 2.5 times the rate for White residents.
Socio-economic reasons, pre-existing comorbidities, work circumstances, inconsistent healthcare access, stress, and decreased immunity, amongst other factors, have been posited as reasons for this shocking disparity. People of color, in particular AA and Hispanics, are more likely to be uninsured and to be frontline workers during the COVID-19 pandemic. This is compounded by the fact that comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, asthma, obesity, and cardiovascular disease are more common in AA and are also associated with higher COVID-19 mortality rates. Emerging evidence suggests that Vitamin D deficiency may represent another risk factor for poor outcomes from COVID-19.
Relevance of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a secosteroid hormone synthesized in the skin following exposure to UVB ultraviolet radiation where it mediates the conversion of 7-dehydrocholesterol to pre-Vitamin D3. Following transport to the liver, it is hydroxylated to 25(OH)D, the primary circulating form typically used to measure serum Vitamin D levels. 25(OH)D is subsequently converted to the biologically active form 1,25, dihydroxy vitamin D in the kidneys by 1-alpha hydrolase. This active form binds to its nuclear Vitamin D receptor to induce the transcription of over 200 genes, affecting a wide range of physiologic functions.
Multiple studies have documented significant Vitamin D deficiency in people of color, especially in AA. Heavily melanized skin retards the synthesis of Vitamin D and necessitates longer periods of sun exposure for adequate synthesis of Vitamin D. Ginde et al. assessed demographic differences and trends of Vitamin D insufficiency in a US population.2Serum 25(OH)D levels were compared over two time periods (1988–1994 and 2001–2004) from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) data base including two large populations (n=18,883 and n=13,369, respectively). Non-Hispanic Blacks had a significantly higher prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency, increasing in severity in the later data base. Recent NHANES data from 2011–2014 further documented the high risk of deficiency in non-Hispanic Blacks. In a recent prospective cohort study of 14,319 subjects, an estimated 65.4% of non-Hispanic Blacks were deficient in Vitamin D, compared to 29% of Hispanics and 14% of non-Hispanic Whites.3
Vitamin D deficiency has been shown to be a risk factor for many of the comorbidities that disproportionately plague AA including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases such as lupus erythematosus, as well as aggressive forms of breast and prostate cancer.4 While the classic role of Vitamin D involves calcium and phosphorus homeostasis for healthy bone metabolism, it exerts a spectrum of pleotropic effects impacting cell growth, differentiation, inflammation, and immune regulation. Healthy levels of Vitamin D have been linked to significantly reduced mortality and improved health outcomes. Numerous investigations document the prolific role of Vitamin D in antimicrobial defense and modulation of the innate and adaptive immune responses. It mediates the induction of key antimicrobial peptides in the respiratory epithelium including cathelicidin (LL37) and beta defensins, which destroy invading organisms. In addition, Vitamin D inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-2, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-6, while promoting Th2 responses by increasing IL-4, IL-5, and IL-10 production, hence skewing T cell responses to a down regulated, anti-inflammatory state.4
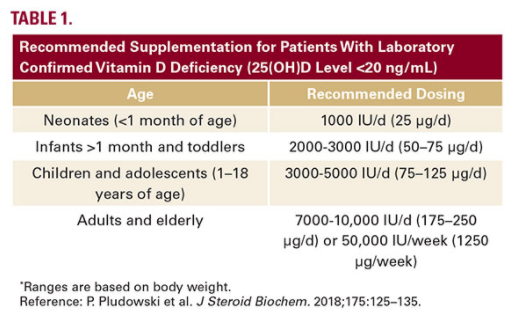
For the general population, the US Institutes of Medicine (IOM) recommends Vitamin D supplementation at doses that vary according to age and are based primarily on bone health. Current IOM supplementation recommendations are 400 IU (10ug) for infants, 600 IU/d (15ug) for children, adolescents, and adults, and 800 IU/d (20ug) for adults aged over 70 years to maintain a 25(OH)D concentration of 20ng/mL or higher. However, in individuals who are deficient in Vitamin D (25(OH)D level <20 ng/ mL), of which patients with skin of color are at a higher risk, supplementation is considerably higher. These recommendations are summarized summarized in Table 1.5
Conclusions