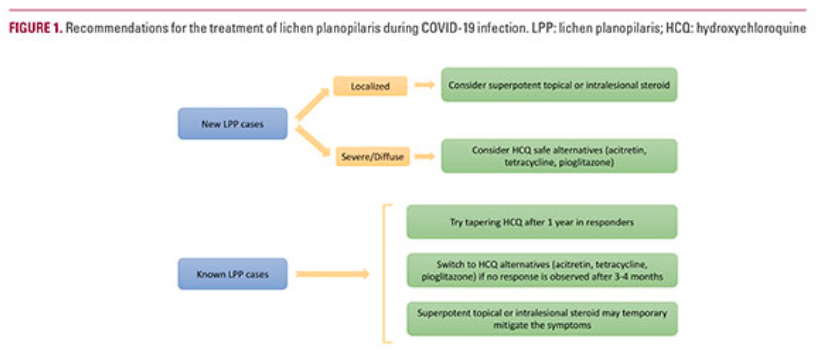
Next Steps in Derm recently published a highlight from the Skin of Color Update Virtual 2020 poster session.
Thin on Top: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the Top Black Hair Loss Videos and Black Hair Loss Treatment Videos on YouTube
Esther B. Henebeng BS¹, Uzoamaka Okoro MD, MSc², Ogechi Ezemma BA¹, Kristina Monteiro PhD¹, Afiya M. Mbilishaka PhD³, Chesahna Kindred MD, MBA4
¹The Warren Alpert Medical School, Brown University, Providence, RI, ²Dwight D. Eisenhower Army Medical Center, Fort Gordon, GA, ³University of the District of Columbia, Washington, DC,4Howard University College of Medicine, Washington, DC
Introduction
Alopecia, or hair loss, is a prevalent concern for both men and women, that has substantial impact on quality of life.¹ Many forms of alopecia in Black women are associated with or worsened by traumatic styling practices such as braiding, weaving, thermal or chemical hair straightening. Therapy is tailored to the specific diagnosis and can include altering haircare practices, topical or oral medications (ex. minoxidil), and in-office treatments (ex. intralesional injections, hair transplant).² However, studies have shown a considerable amount of Black women are concerned physicians may not understand their hair and fail to engage in discussions about hair issues for this reason.³ More than 50% of Black women experience hair loss, with a majority of women searching for treatment options from online resources instead of seeking care from a primary care physician or dermatologist.4 YouTube is one of the most frequently used websites, with 77% of Black adults using the social media platform.5 Although dermatologists have established an online presence, approximately 75% of the top dermatology-related videos on YouTube are from non-dermatologist sources.6 This is particularly concerning because videos from third parties have been found to suffer from incomplete information, overall poor quality, and can contribute to potential harm or delay in appropriate diagnosis.6,7
Behbahani et al showed that YouTube is a highly utilized resource for hair loss treatment information, but found no significant difference between the overall quality of board certified dermatologist and non-physician videos.7 However, videos from lay media or individuals have been shown to have lower accuracy in comparison to videos from health care sources.8 Examination of top YouTube videos regarding “hair” and “hair loss” demonstrated very few videos displaying more textured or tightly coiled hair types associated with Black hair. Consequently, our project will evaluate the accuracy, quality, viewer engagement, and viewer experience of “Black hair loss” and “Black hair loss treatment” videos on YouTube.
Objectives
-
- Evaluate the accuracy of Black hair loss and Black hair loss treatment videos on YouTube in comparison to published, peer-reviewed articles found via PubMed literature review
- Compare the quality, viewer engagement, and viewer experience of non-health care and health care sources
Methods
YouTube was searched for the following: “Black hair loss” and “Black hair loss treatment” on June 18, 2020. The first 60 videos per search term were examined and categorized into health care or non-health care sources. Two independent raters evaluated each video with four validated instruments: 1) Accuracy in Digital Health, 2) Accuracy Scale, 3) Armstrong Viewer Assessment, and 4) Global Quality Scale.8 Viewer engagement ratio was defined as (number of likes + dislikes + comments) / total views. Discrepancies between coders were resolved through discussion. Duplicate and non-English videos were excluded. Significant differences between health care and non-health care sources were determined using Mann- Whitney U test.
Results
Our search yielded a total of seventy-eight unique YouTube videos. Three videos made no claims to assess accuracy and were excluded from analysis (*).
Twenty-two (28.2%) of the videos were from health care sources and fifty-six (71.8%) from non-health care sources. Health care sources were made up of dermatologists, nondermatologist medical doctors, and university/professional organizations. Non-health care sources included individuals, hairstylists, companies, and lay media. Speakers in 45 of the YouTube videos (57.7%) self-identified as Black based on video content or a publicly accessible social media post. Of the 45, there were only 2 videos categorized as health-care sources that had a self-identified Black speaker.
Discussion
There are over 20 million total views for the top 78 videos on Black hair loss and Black hair loss treatment. These videos typically range from 1 minute to 10 minutes long, with varying levels of engagement. Videos by Black speakers were found to have higher levels of engagement (0.02 ± 0.02, P = <0.001). Many of the videos by non-health care sources were inaccurate or made claims with no evidence supported by PubMed literature review. A few speakers encouraged viewers to try potentially harmful practices to stimulate hair growth (ex. Vicks VapoRub to scalp, prolonged protective styles, intermittent fasting or detoxing). When compared to non-health care sources, health care sources had lower mean numbers of views (81,965 vs 330,113, P = 0.008). Furthermore, health care sources were less engaging than non-health care sources (0.01±0.01 vs 0.02 ±0.02, P = 0.012), but more accurate (Accuracy in Digital Health: 3.77 ±0.43 vs 2.00 ±1.57, P = <0.001; Accuracy Scale: 3.91 ±0.30 vs 2.15 ±1.25, P = <0.001). Most inaccuracies from health care sources were primarily associated with the promotion of a product or treatment that does not have proven efficacy. Fewer inaccuracies were related to incorrect comments regarding hair physiology and causes of hair loss. Nevertheless, health care sources provided a superior viewer experience (Armstrong Viewer Assessment: 3.09 ±0.53 vs 2.55 ±1.01, P = 0.023) and were of higher quality (Global Quality Scale: 3.64 ±0.85 vs 2.47 ±1.09, P = <0.001) in comparison to non-health care sources.
Conclusion
-
- Social media platforms can improve a patient’s access to care and serve as an inclusive environment to share educational content.
- Our findings suggest that many of the top YouTube videos on “Black hair loss” and “Black hair loss treatment” are inaccurate.
- Health care sources should be cautious when suggesting products or treatments that are not evidence-based.
- Even though health care sources were more accurate, they had less viewer engagement when compared to non-health care sources.
- The data supports the need for further diversity in dermatology as Black speakers were found to have greater levels of engagement and participation.
- Lastly, our results also underscore the need for dermatologists to work in tandem with non-health care sources (ex. hairstylists) who may have a larger following on social media in order to dispel misinformation online.